South Korean researchers have publicly disclosed an encryption flaw within the Rhysida ransomware encryptor, permitting the introduction of a Home windows decryptor to get better information without spending a dime.
Rhysida is a ransomware operation that introduced in mid-2023 and is infamous for concentrated on healthcare organizations, disrupting their an important operations, and promoting delicate affected person data.
In November 2023, the FBI and CISA warned in regards to the gang’s opportunistic assaults in opposition to a large spectrum of business sorts, together with healthcare, army, cultural, and power organizations.
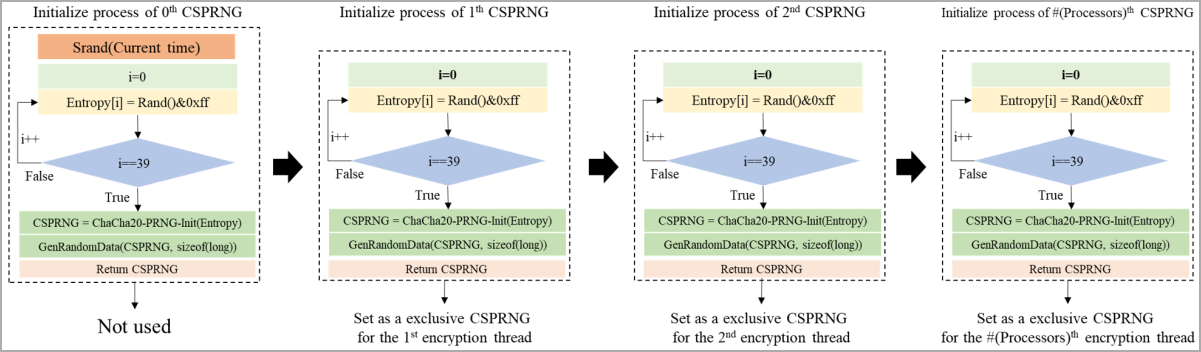
South Korean researchers, together with staff of the Korean Web & Safety Company (KISA), analyzing Rhysida discovered an implementation vulnerability within the ransomware’s encryption scheme, in particular, the random quantity generator (CSPRNG) that is helping generate the original personal (encryption) key in every assault.
By way of exploiting the flaw, the analysts may get better the interior state of CSPRNG throughout the assault and use it to create a legitimate key to opposite the knowledge encryption.
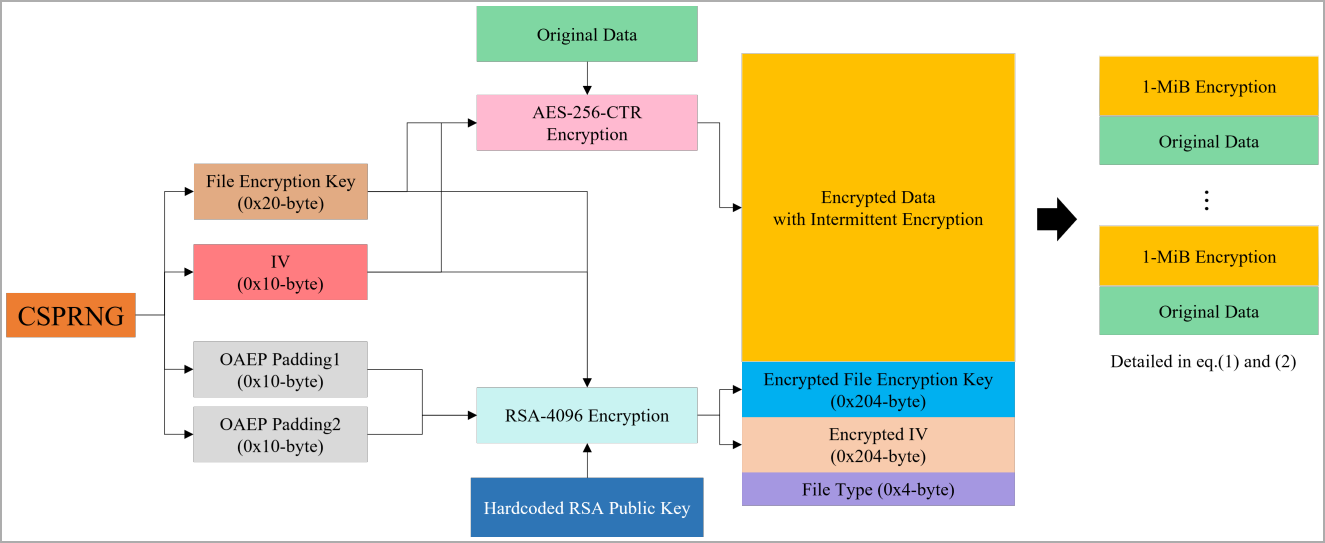
Rhysida’s use of intermittent encryption, a tactic of most effective encrypting portions of the information whilst leaving others in plaintext, used to be crucial in shaping the decryption way, because the researchers needed to perceive the encryption development and follow the proper key selectively to the affected document portions.
Predictable seed price
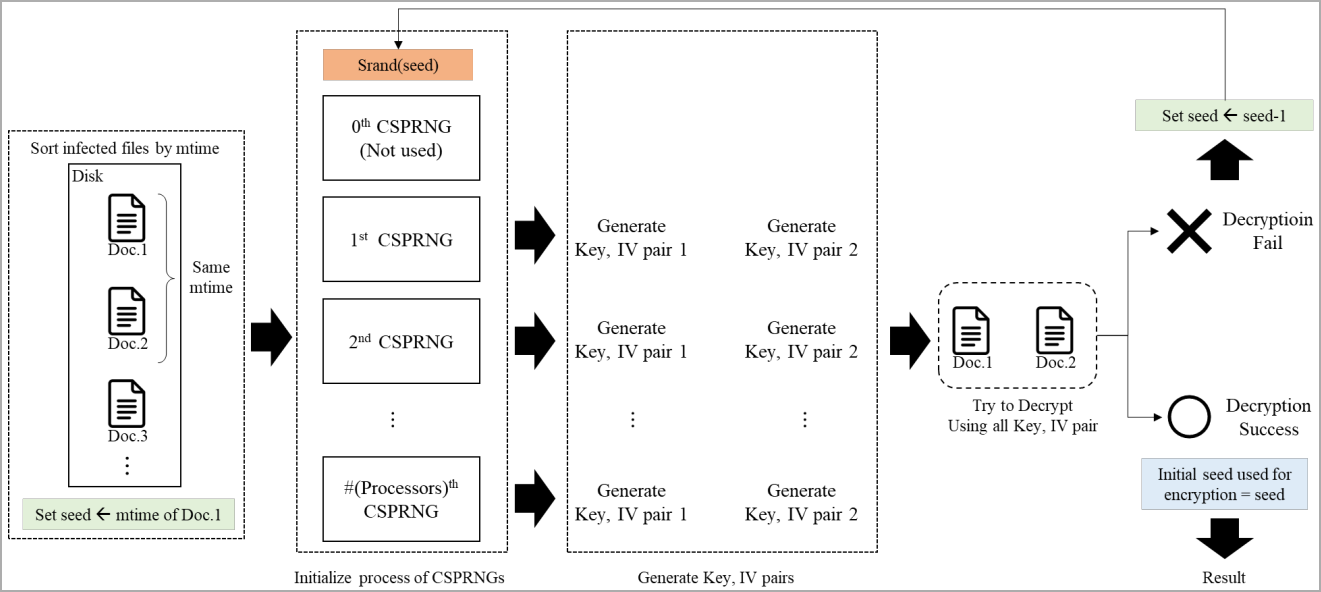
Rhysida’s misguided price technology gadget depends upon deriving the 32-bit seed price from the gadget’s present time, which the researchers say limits the hunt house to a computationally viable scope.
Rhysida makes use of this price to generate the personal encryption key and initialization vector however lacks different high-entropy knowledge resources to be sure that the seed price is unpredictable, making it guessable through having a look into logs or different knowledge indicating the time of the an infection.
Armed with this information, the researchers advanced a technique that systematically regenerates the CSPRNG state through testing other seed values inside the anticipated vary.
As soon as the proper price is located (through validating that it may decrypt knowledge), all next random numbers utilized by the ransomware to encrypt information may also be simply predicted, so all locked knowledge may also be retrieved with out requiring the real personal key.
The decryption works through as it should be regenerating the similar encryption key and preliminary vector used throughout the unique encryption procedure after which making use of a counter-mode (CTR) encryption procedure to the encrypted segments of the information.
This technique successfully reverses the encryption, restoring the unique plaintext with no need the attacker’s personal key, exploiting the symmetric assets of CTR mode the place the encryption and decryption operations are equivalent.

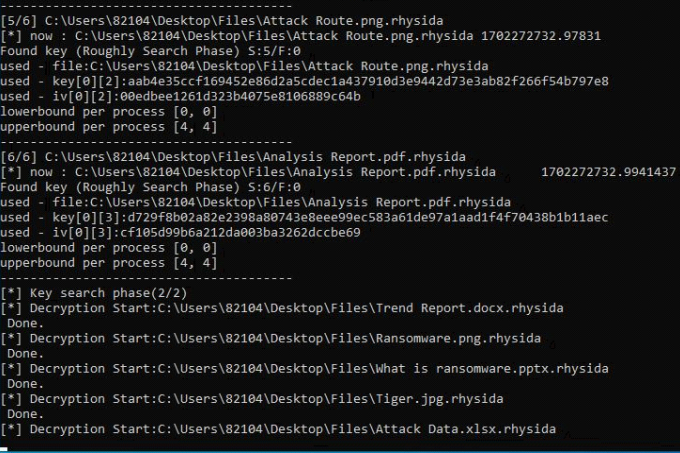
An automatic decryption device for Home windows is to be had on KISA’s site in conjunction with a technical paper revealed ultimate Friday, with utilization directions in Korean and English.
Sufferers of the Rhysida ransomware would possibly use the device to take a look at to decrypt their information without spending a dime, however BleepingComputer can not ensure the device’s protection or effectiveness.
Ransomware professional Fabian Wosar advised BleepingComputer that this decryptor most effective works for encrypted information through the Rhysida Home windows encryptor and can not decrypt information encrypted on VMware ESXi or by means of its PowerShell-based encryptor.
Flaw privately exploited for months
The Rhysida encryption flaw has been privately used for months through cybersecurity corporations and governments international since no less than Would possibly 2023.
“There is going any other one. They’re clearly no longer the primary person who discovered this vulnerability,” explains Wosar in a thread on X
“This used to be independently discovered through no less than 3 different events, who selected to flow into it in personal as an alternative of in search of newsletter and alerting Rhysida about their drawback.”
“As to who the ones events are: Avast discovered it in October ultimate yr, the French CERT authored and revealed a personal paper about it in June, and I discovered the vulnerability in Would possibly ultimate yr.”
Wosar advised BleepingComputer that petabytes of knowledge on masses of machines were effectively decrypted the use of this flaw since he came upon it in Would possibly.
When BleepingComputer contacted the South Korean researchers to invite why the flaw used to be publicly disclosed, they shared the next commentary.
So far as we all know, many cyber safety firms are disclosing decryption ways on their blogs/githubs/and many others. And this unquestionably is helping to mitigate the wear and tear. We advanced the decryption device in collaboration with KISA and made up our minds to free up the paper to successfully show it. We’re publishing our detailed analysis within the hope that it is going to give a contribution to the resilience of ransomware sufferers.
Then again, now that the flaw is public, Wosar warns that the ransomware operation will most likely repair the computer virus in days, making it unimaginable to get better information with out paying a ransom call for.

